40 collision theory 16.1 worksheet answer key
Aug 06, 2021 · Collision Theory Worksheet Answer. Kinematic Equations Worksheet Math Worksheets #1 Answers Physical Science: ... half life answer key,contains student exploration collision theory worksheet .... (a): Review the group's answer to question #2 on the Explore 2 worksheet. ... Collision theory helps explain why these factors affect reaction rate..
Answer Key 1.C 2.The laws of nature are written as mathematical equations because they show a precise relationship between physical quantities and can be used to make predictions about future experiments. 3.A scientific hypothesis is more than just a guess, it is a prediction based on reason, evidence, and logic. 4.B 5.C
a separate machine-scorable answer sheet. Total testing time is two hours and fifty minutes; there are no separately timed sections. Following are some general test-taking strategies you may want to consider. Read the test directions carefully, and work as rapidly as you can without being careless. For each question, choose the best answer from the
Collision theory 16.1 worksheet answer key
6. Calculate the momentum value of ... . (Include appropriate units on your answers.) a. ... a 2.0-kg brick moving through the air at 12 m/s. p = m•v = (2.0 kg)•(12 m/s) = 24 kg•m/s b. ... a 3.5-kg wagon moving along the sidewalk at 1.2 m/s. p = m•v = (3.5 kg)•(1.2 m/s) = 4.2 kg•m/s 7.
Age range: 14-16. Worksheet for middle to higher ability GCSE pupils to explain collision theory using a series of diagrams. Includes temperature, concentration, gas pressure, surface area and catalysts. Report this resource to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions. Our customer service team will review your report and will be in ...
1 CHAPTER . Scene Size-Up . 11 . HANDOUT 11-1: Evaluating Content MasteryStudent's Name. EVALUATION . CHAPTER 11 QUIZ . Write the letter of the best answer in the space provided. _____ 1. Which of the following is NOT a part of the scene sizeup?- A. Determining the mechanism of injury . B. Determining the number of patients C. Establishing an ...
Collision theory 16.1 worksheet answer key.
ANSWER KEY MOMENTUM FORMULA & STUFF FROM THE PAST: p = m v, TKE = ½mv2, d = v t 1. An ostrich with a mass of 146 kg is running to the right with a velocity of 17 m/s. a. Calculate the momentum (in kg m/s) of the ostrich. Ans. p = m v = 146 kg 17 m/s = 2482 kg m/s b. Calculate the kinetic energy (in J) of the ostrich. Ans. TKE = ½ mv2 = ½
1 5 = 400,000 pianos Estimate 3 tunings per day per tuner, with 200 work days per year. Number of pianos tuned each year (per tuner) = (3)(200) = 600 Number of tuners == 36. diameter = 3.8 cm Find the number of balls that can fit along the length and width. l = 4 m w = 4 m h = 3m 4 m × 0. 1 1 2 = = 1 1 = Holt Physics Solution Manual
16. Momentum before collision= Momentum after collision p before = p after (Elastic) m 1 v 1 + m 2 v 2 = m 1 v 1 ’ + m 2 v 2 ’ ’ (Inelastic) m 1 v 1 + m 2 v 2 = (m 1 + m 2) v. 17. A block with mass 60 kg and velocity 50 m/s moving along a frictionless surface collides with a stationary block with a mass 40 kg. After the elastic collision ...
Collision Theor Fill in the blanks below using each word once. —concenlegtion 16.1 Particles can only react if they with enough for the reaction to take place. This is called There are four factors that can change the rate of a reaction; area and the use of a suitable
1 para = 3.1104 ×1014 years 365 1.2 y 5 ea d r ays × 1 24 da h y × 1 × 1M 10 h 6 h 365 1.2 y 5 ea d r ays × 1 24 da h y × 36 1 0 h 0s × 1 × 1 1 n 0 s −9s Convert from years to megahours by multiplying the time by the first conversion expression. 1 para = 3.1104 ×1014 years × 365 1.2 y 5 ea d r ays × 1 24 da h y × 1 × 1M 10 h 6 h =
Worksheet - Using Measurements Worksheet - Units & Unit Conversions Lab - Density of Pennies Article - "The Crash of Flight 143" Electrons in Atoms - Ch. 4. Worksheet - Waves & Particles Worksheet - Bohr Model Worksheet - Quantum Model Worksheet - Electron Configuration Worksheet - Stability & Electron Configuration
Time: 1 -2 class periods Lesson Description Key Essential Questions Learning Outcomes Prior Student Knowledge Expected Lesson Materials Standards Alignment In this lesson, students will use Collisions to explore the three types of intermolecular forces (IMFs): (1) London Dispersion Forces, (2) dipole-dipole, and (3) hydrogen bonding. 1.
2 A N S W E R K E Y True/False Short Answer 1. Companies common to most fire departments include (Students should include five of the following): (1) Engine company:An engine company is responsible for securing a water source, deploying handlines, conducting search-and-rescue
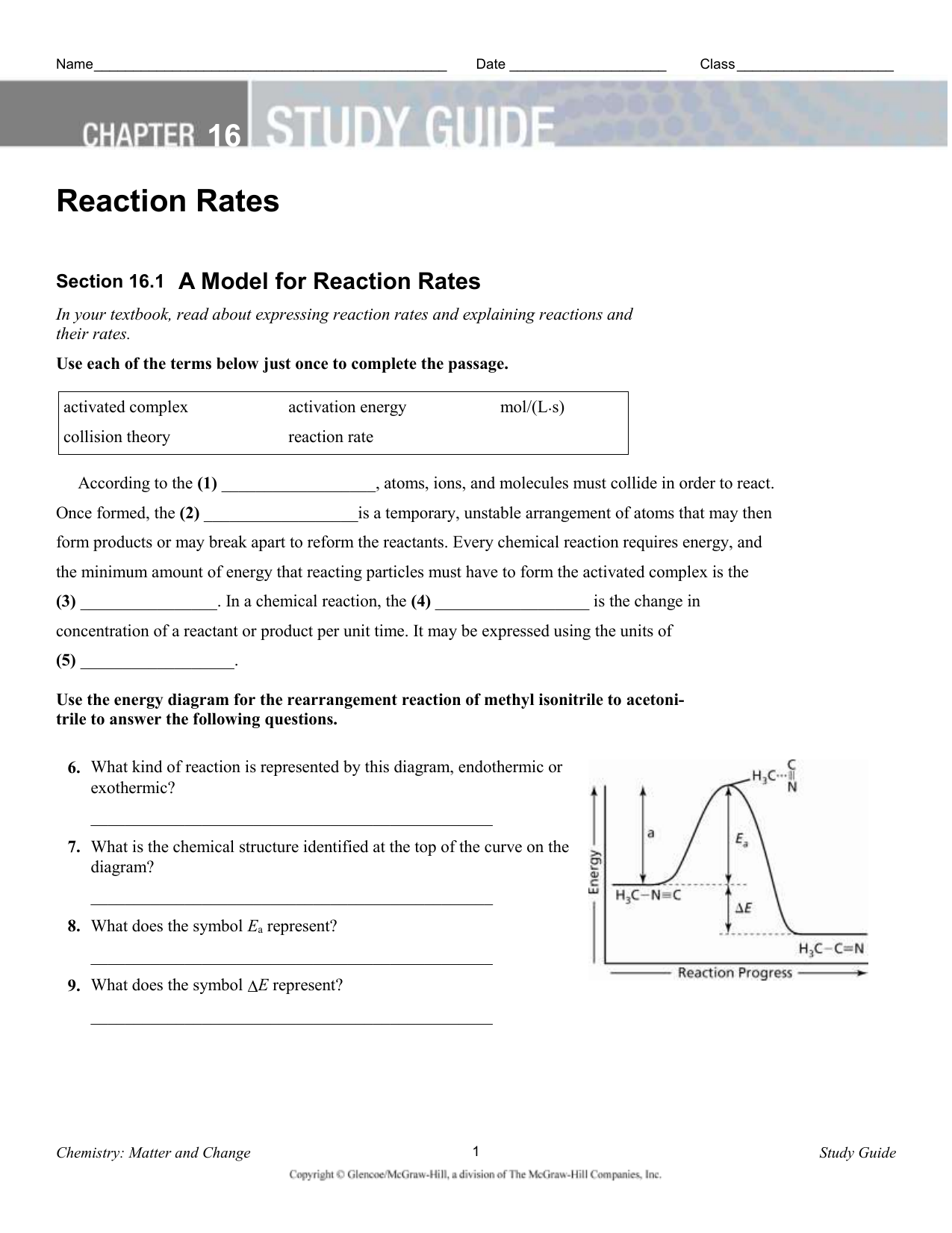
16.1 A Model for Reaction Rates MAIN Idea Collision theory is the key to understanding why some reactions are faster than others. 16.2 Factors Affecting Reaction Rates MAIN Idea Factors such as reactivity, concentration, temperature, surface area, and catalysts affect the rate of a chemical reaction. 16.3 Reaction Rate Laws MAIN Idea The ...
Answers may vary. Different alleles are possible within the population due to random mutations that may occur. In addition, the food supply may differ from one organism to another causing different body mass. 4. Refer to graph A of Model 1. a. How is the population that has experienced selection different from the original population?
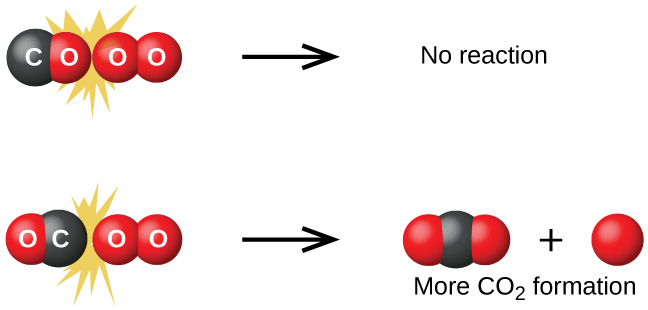
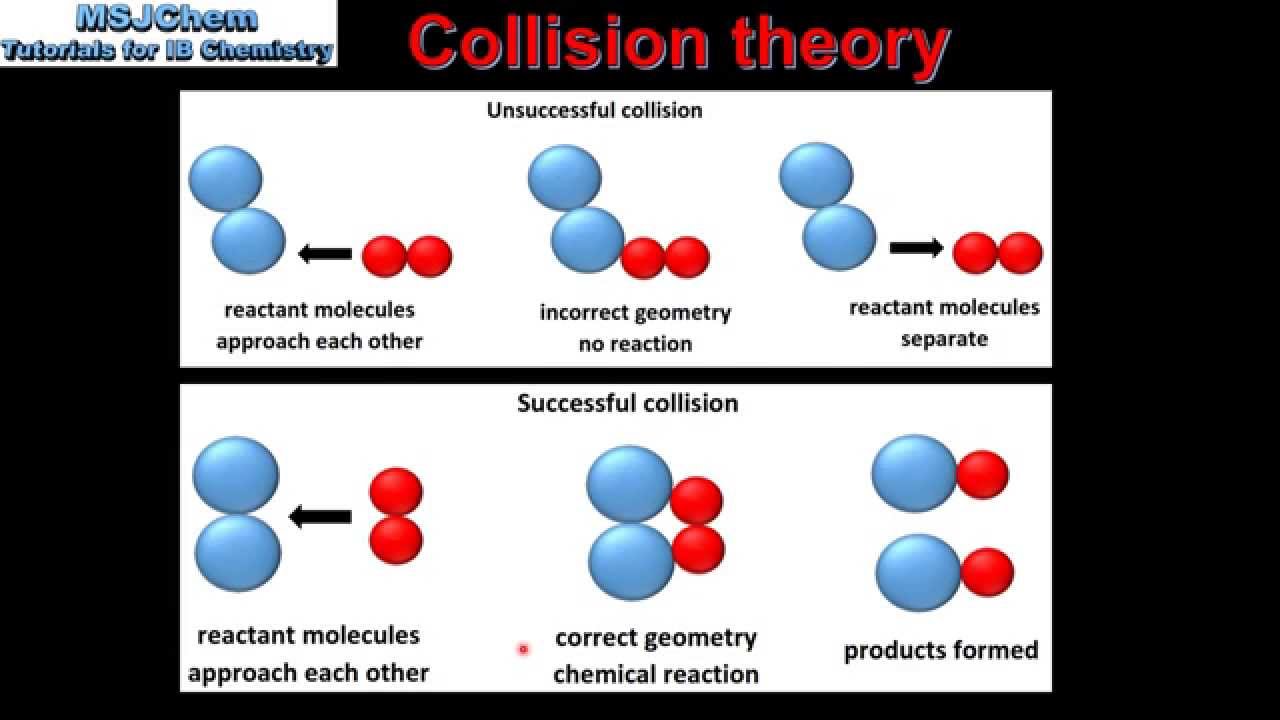
collision theory worksheet name: _____ key _____ 15. explain collision theory. collision theory is a way to explain why different reactions occur at different rates. it states that for a reaction to occur, particles need to collide with enough energy and hit with the correct orientation. 16.
Answer: See Answers above. In a collision, the impulse encountered by an object causes and is equal to the momentum change of the object. For objects being brought to rest, the change in momentum is simply equal to the original momentum. An object with twice the momentum would require twice the impulse to stop it.
Collision theory Worksheet Answers Key Elegant Chemistry 12 one of Free Worksheets - Free, printable main idea worksheets to develop strong reading .... In this worksheet, you will learn what chemists mean by collision theory, and how it explains the speed of a chemical reaction..
Each Collisions game comes with free chemistry resources to use in the classroom including Game Guides, Quickstart Guides, and Student Activities. Resources available for your chemistry classroom for Atoms, Ions, Ionic Bonding, Covalent Bonding, IMFs, Phase Change, and Acids & Bases.
If a 9.7-gram bullet is fired into the center of a 1.1-kg block of wood and it rises upward a distance of 33 cm, then what was the pre-collision speed of the bullet? Answer: 2.9 x 10 2 m/s Here is another instance in which momentum principles must be combined with content learned in other units in order to complete an analysis of a physical ...
= 0.16 kg Paraphrase The mass of the hockey puck is 0.16 kg. 12. Given m = 425 g v G = 18.6 m/s [214°] Required momentum vector diagram Analysis and Solution The momentum of the soccer ball is in the direction of its velocity. So use the scalar form of p G = mv G to find the magnitude of the momentum.
Worksheet 15: Hydrocarbons MCQs Worksheet 16: Introduction to Organic Chemistry MCQs Worksheet 17: Ionic Equilibria MCQs Page 1/10. Read PDF Collision Theory Answer Key Worksheet 18: Lattice Energy MCQs Worksheet 19: Moles and Equations MCQs Worksheet 20: Nitrogen and Sulfur MCQs Worksheet 21: Organic and Nitrogen Compounds MCQs Worksheet 22 ...
Collision Lab - PhET Interactive Simulations
Collision Theory Worksheet Answers. 1) Explain why all reactions have an activation energy, using your knowledge of collision theory. All reactions have an activation energy because energy is required to make the reactants combine in a way that will cause the reaction. No chemical process can take place without having at least a little energy ...
1. Click a bookmark on the left. To print a part of the book 1. Click the Print button. 2. When the Print window opens, type in a range of pages to print. The page numbers are displayed in the bar at the bottom of the document. In the example below, "1 of 151" means that the current page is page 1 in a file of 151 pages.
©2010 by Pearson Education, Inc. CHAPTER 1 Emergency Medical Care Systems, Research, and Public Health Prehospital Emergency Care, 9th Ed. CHAPTER 1 ANSWER KEY HANDOUT 1-1: Chapter 1 Quiz 1. C 4. D 7. A 9. A 2. C 5. C 8. C 10. C 3. D 6. B HANDOUT 1-2: In the Field 1.
Determine the post-collision speed of the combination of brick and cart. (2.9 kg)•(26 cm/s) = (2.1 kg + 2.9 kg)•v 75.4 kg•cm/s = (5.0 kg)•v v = 15.1 cm/s 3. A 98-kg fullback is running along at 8.6 m/s when a 76-kg defensive back running in the same direction at 9.8 m/s jumps on his back. What is the post-collision speed of the two players
A plot of ln(k) versus 1/T was constructed that resulted in a straight line with the slope of -1.10 x 10 4 K and a y intercept of 33.5. Determine the E a. E a = 91454 J . Determine A. A = 3.54 x 10 14 . Calculate k at 298K. k = 0.0330 s-1 . Consider NO 2(g) + CO (g) → NO (g) + CO 2(g) If the activation energy is 125 kJ/mol, and ΔE for the ...
An object with a mass of 0.10 kg makes an elastic head-on collision with a stationary object with a mass of 0.15 kg. The final velocity of the 0.10 kg object after the collision is —0.045 m/s and the final velocity of the O. 15 kg object after the collision is 0.16 m/s. What was the initial velocity of the O. 10 kg object? a. 0.16 m/s .06 TMs
Unformatted text preview: COLLISION THEORY WORKSHEET KEY 1. Explain why all reactions have an activation energy using your knowledge of collision theory. All reactions involve the breaking and reforming of chemical bonds. This takes a certain amount of energy called the activation energy. This energy comes from the kinetic energy involved in ...
Explain your reasoning in terms of the nature of the collision. 4. Did a reaction take place between Reactant A and Reactant B in Scenario 4? Why or why not? Explain your reasoning in terms of the nature of the collision. 5. Based on your responses to Key Questions 1-4 and your reasoning, what insight has your team gained about the term ...
Created Date: 1/7/2016 8:52:12 PM
Description. Have students demonstrate their understand of collision theory and the impact of temperature, concentration, surface area and catalysts on the rate of a reaction. The worksheet is completing paragraphs with the terms given. Answers included.
























0 Response to "40 collision theory 16.1 worksheet answer key"
Post a Comment