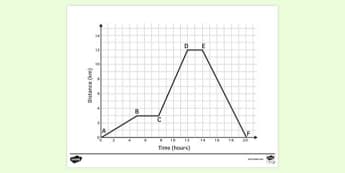
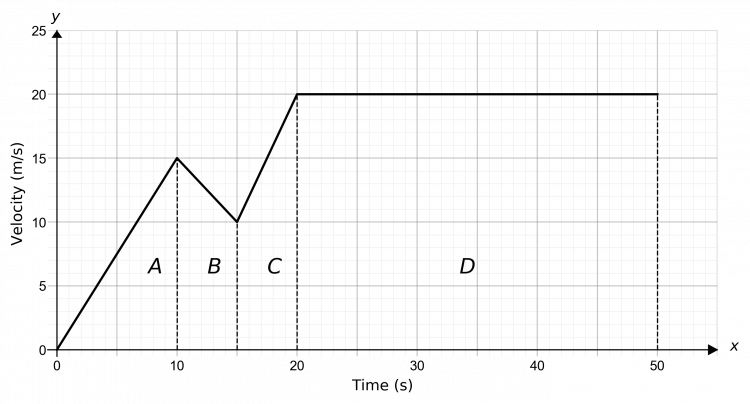
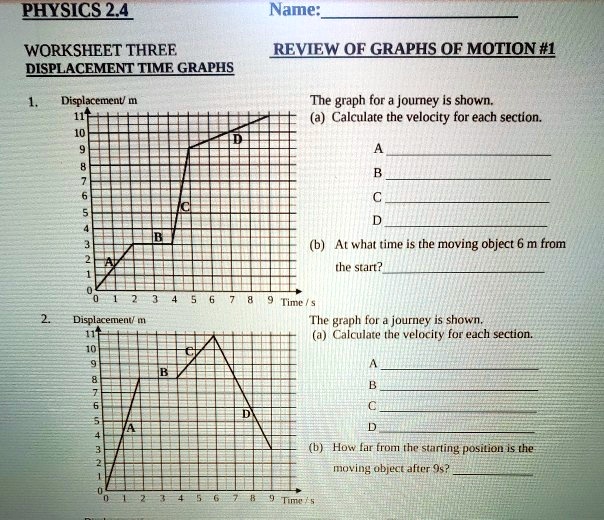
45 velocity time graph worksheet
physics.info › motion-graphs › practiceGraphs of Motion - Practice – The Physics Hypertextbook When acceleration is positive, the velocity-time graph should have a positive slope and the displacement-time graph should bend upward. When acceleration is negative, the velocity-time graph should have a negative slope and the displacement-time graph should bend downward. When acceleration is zero, all three graphs should lie on the horizontal ... Speed versus Velocity - Physics Classroom Speed, being a scalar quantity, is the rate at which an object covers distance. The average speed is the distance (a scalar quantity) per time ratio. Speed is ignorant of direction. On the other hand, velocity is a vector quantity; it is a direction-aware quantity. The average velocity is the displacement (a vector quantity) per time ratio.
Interpret motion graphs (practice) | Khan Academy Interpreting change in speed from velocity-time graph. Practice: Interpret motion graphs. This is the currently selected item. Worked example: Motion problems with derivatives. Practice: Motion problems (differential calc) Next lesson. Rates of change in other applied contexts (non-motion problems) Interpreting change in speed from velocity-time graph . Worked example: …
Velocity time graph worksheet
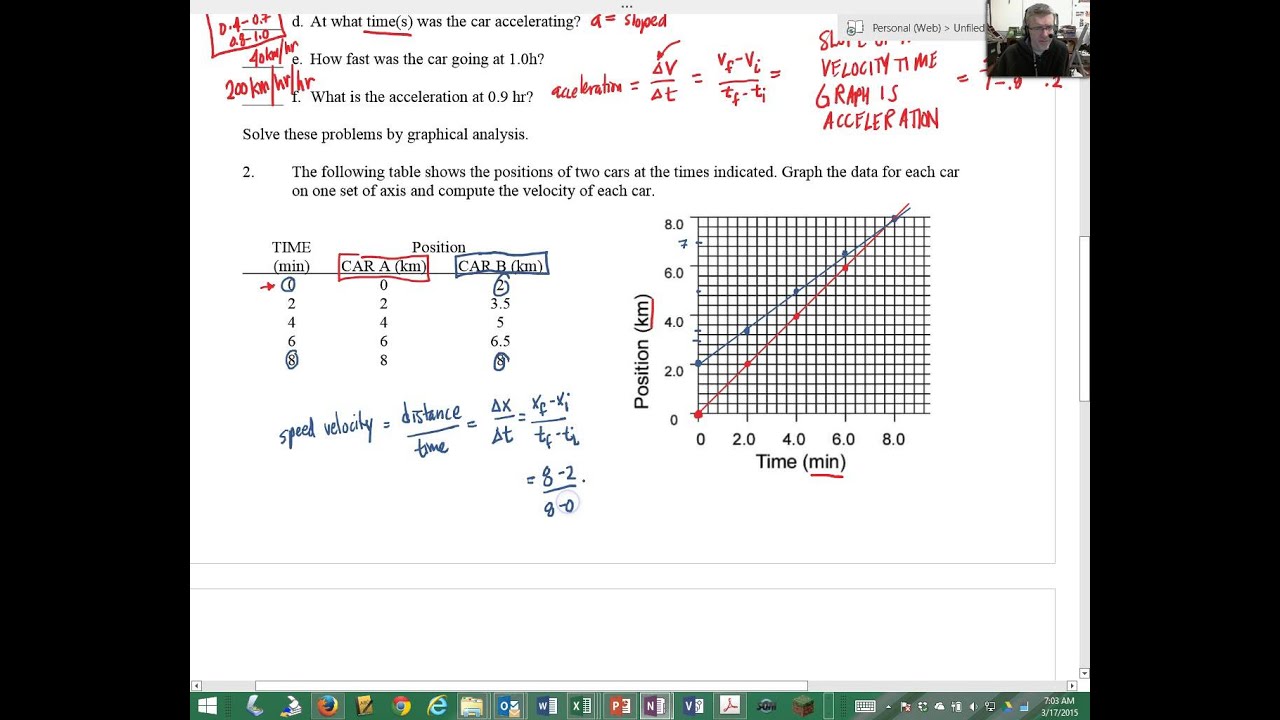
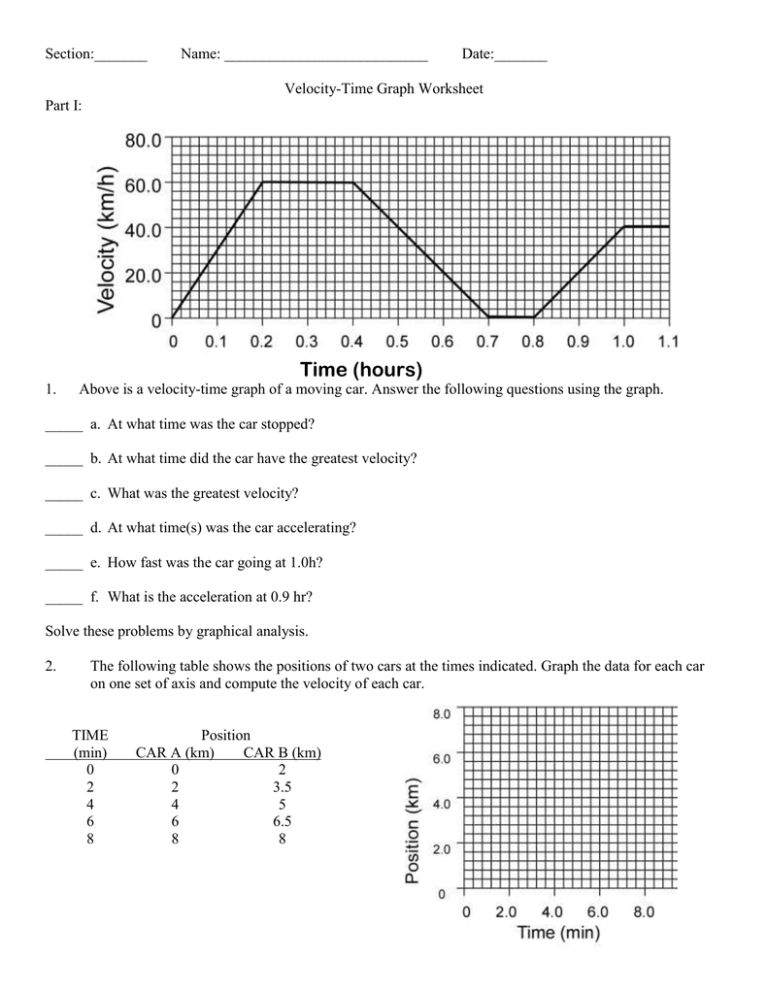
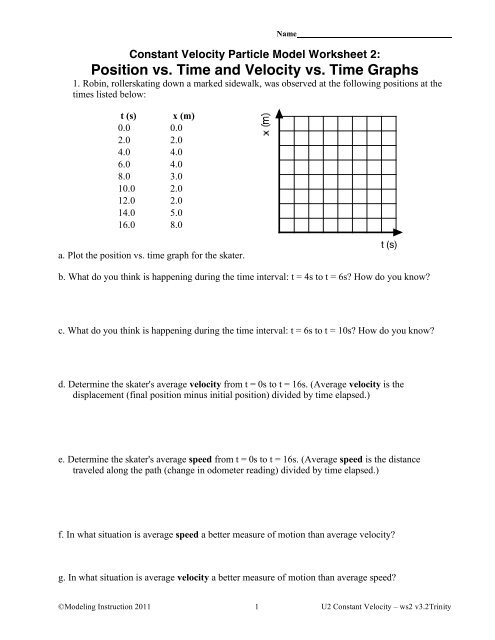
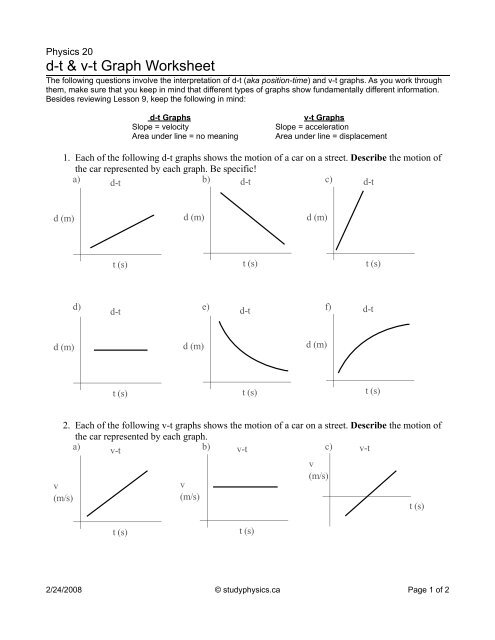
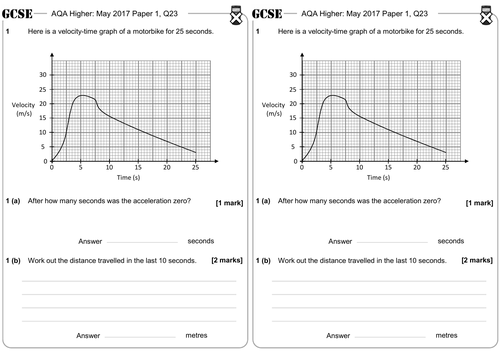
› reviews › 1D-Kinematics1D Kinematics Review - with Answers - Physics Classroom Furthermore, a negative velocity would be a line plotted in the negative region of the graph; a positive velocity would be a line plotted in the positive region of the graph. a. An object at rest (v = 0 m/s) is represented by a line located on the time axis (where v = 0 m/s). › cms › lib9Unit 2 Kinematics Worksheet 1: Position vs. Time and Velocity ... a. What does the slope of a position time graph tell you about the motion of an object? It is the average velocity over the interval of time the slope is taken b. Looking at the velocity time graphs (Questions 4 and 5), determine the units for a square of area on the graph. units of the area under v-t curve are (m/s) x (s) = m c. Kinematic Equations: Sample Problems and Solutions - Physics … Kinematic equations relate the variables of motion to one another. Each equation contains four variables. The variables include acceleration (a), time (t), displacement (d), final velocity (vf), and initial velocity (vi). If values of three variables are known, then the others can be calculated using the equations. This page demonstrates the process with 20 sample problems and …
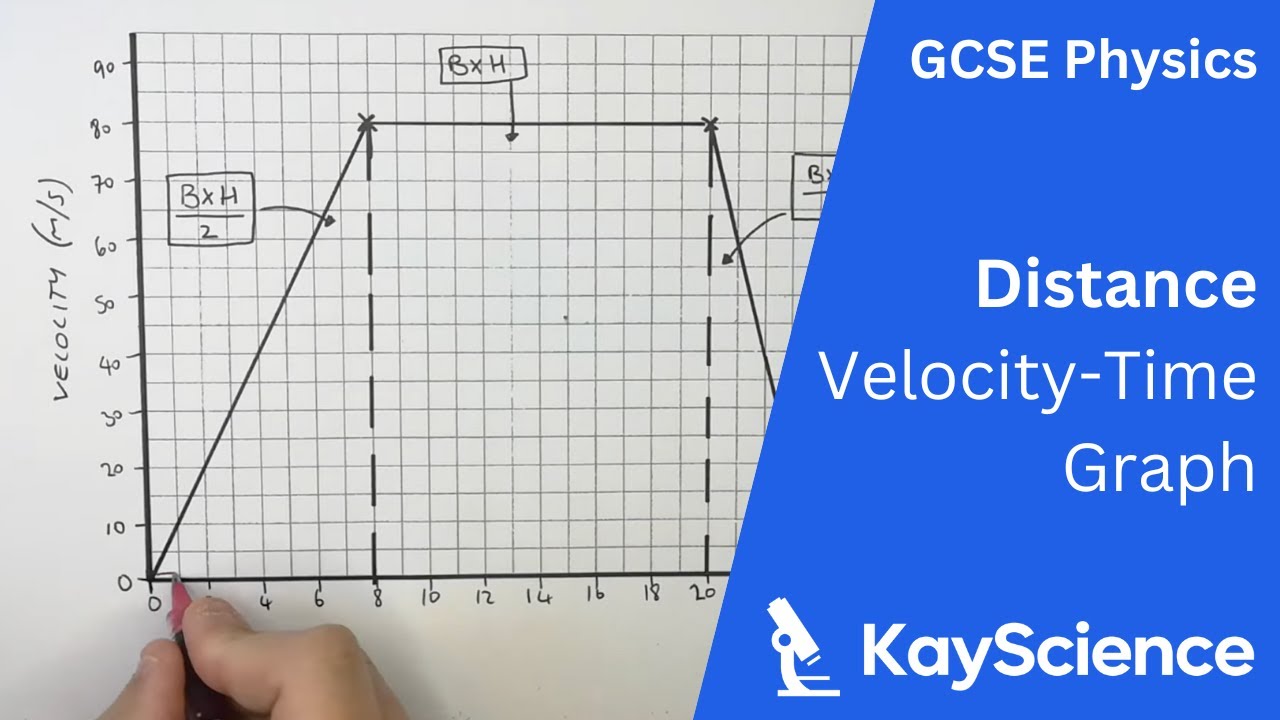
Velocity time graph worksheet. › cms › lib6Practice Problems: Speed, Velocity, and Acceleration Velocity – Speed in a given direction. Frame of reference – A background used to judge motion or speed. Instantaneous Speed – Speed at a given moment in time. Speed – amount of distance traveled in a certain amount of time. Average Speed – total distance divided by total time. Time-Distance Graph – graph that shows speed of an object openstax.org › books › university-physics-volume-13.1 Position, Displacement, and Average Velocity - OpenStax We can graph Jill’s position versus time as a useful aid to see the motion; the graph is shown in Figure 3.5. Figure 3.5 This graph depicts Jill’s position versus time. The average velocity is the slope of a line connecting the initial and final points. › physics › acceleration-time-graphAcceleration Time Graph - Understanding, Area and Examples The acceleration time graph is the graph that is used to determine the change in velocity in the given interval of the time. In the acceleration vs time graph on the x-axis you have the time taken by the object and on the y-axis acceleration of the object, in which the area under the graph gives you the change in velocity of the object over the given period of the time. › class › vectorsRelative Velocity and River Boat Problems - Physics Classroom The time to cross the river is dependent upon the velocity at which the boat crosses the river. It is only the component of motion directed across the river (i.e., the boat velocity) that affects the time to travel the distance directly across the river (80 m in this case).
Kinematic Equations: Sample Problems and Solutions - Physics … Kinematic equations relate the variables of motion to one another. Each equation contains four variables. The variables include acceleration (a), time (t), displacement (d), final velocity (vf), and initial velocity (vi). If values of three variables are known, then the others can be calculated using the equations. This page demonstrates the process with 20 sample problems and … › cms › lib9Unit 2 Kinematics Worksheet 1: Position vs. Time and Velocity ... a. What does the slope of a position time graph tell you about the motion of an object? It is the average velocity over the interval of time the slope is taken b. Looking at the velocity time graphs (Questions 4 and 5), determine the units for a square of area on the graph. units of the area under v-t curve are (m/s) x (s) = m c. › reviews › 1D-Kinematics1D Kinematics Review - with Answers - Physics Classroom Furthermore, a negative velocity would be a line plotted in the negative region of the graph; a positive velocity would be a line plotted in the positive region of the graph. a. An object at rest (v = 0 m/s) is represented by a line located on the time axis (where v = 0 m/s).






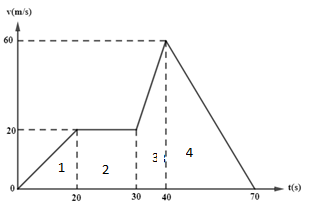
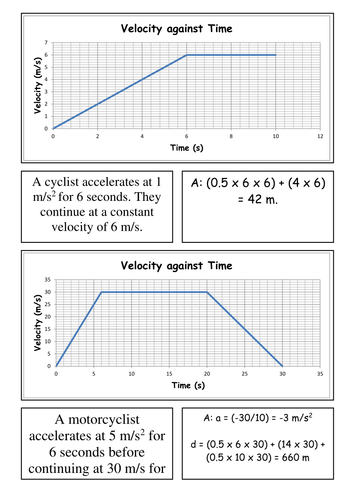



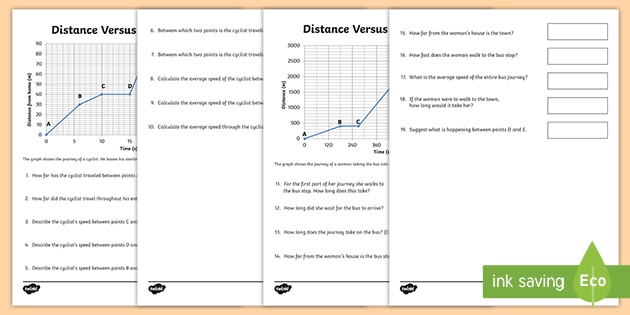




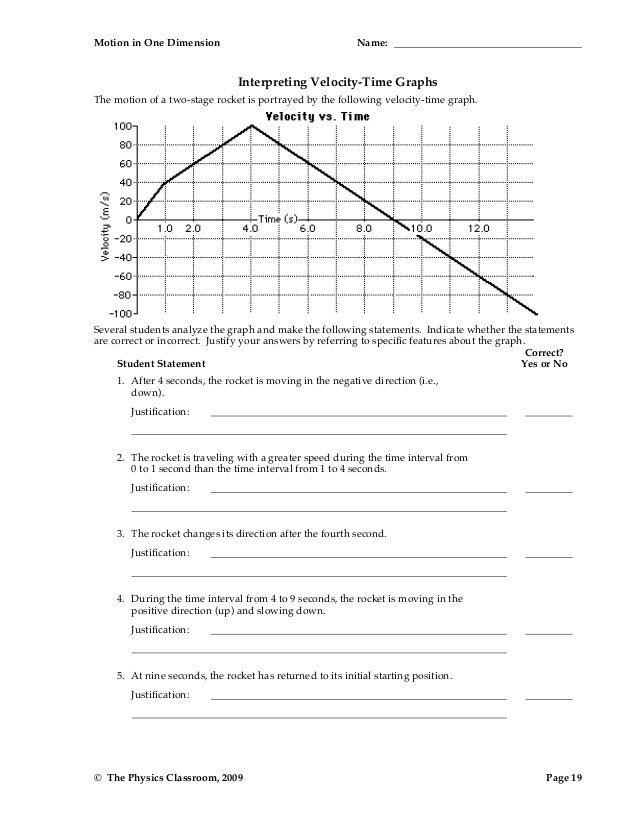
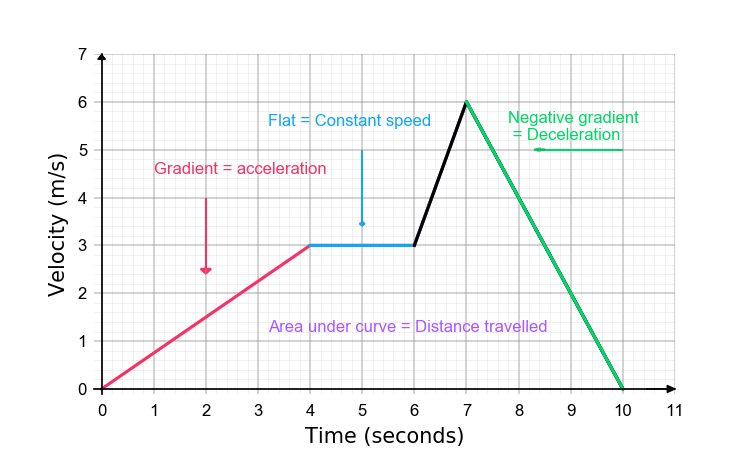







0 Response to "45 velocity time graph worksheet"
Post a Comment