42 12.2 the structure of dna worksheet answers
PDF TCSS Biology Unit 2 Genetics Information - Troup structure and function of DNA. DNA Replication Student Practice (12.2) -Comprehension , questions for practice following lecture. DNA Replication Coloring (12.2) -Includes color-coding and , comprehension questions , DNA Replication Worksheet -Students will draw pictures that , correspond to the descriptions of the replication process. worksheet 1 dna structure 13 Best Images Of 12.2 The Structure Of DNA Worksheet Answers - DNA, , DNA Structure And Mutations - SCIENCE WITH MISS ALOLABI, alolabi-science.weebly.com, dna structure science normal except direction else something why there which directionality, Chromosome structure (labeling). Chromosome labeling. Dna coloring,
12.2 WS- Answers.doc - Answers 12.2 The Structure of DNA... - Course Hero Answers 12.2 The Structure of DNA The Components of DNA For Questions 1-5, complete each statement by writing in the correct word or words. 1. The building blocks of DNA are nucleotides. nucleotides . 2. Nucleotides in DNA are made of three basic components: a sugar called deoxyribose, a phosphate group,and a nitrogenous base.
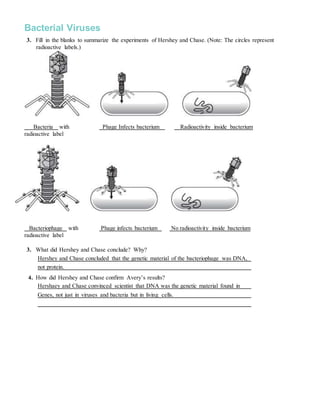
12.2 the structure of dna worksheet answers
PDF Cell Division Worksheet - lancaster.k12.oh.us 18. Which symbol represents a cell dividing by mitosis? (Circle all that apply) 2n 2n 2n n n n n + n 2n , Use figure 12.2 below to answer the following questions. Write the letter, or letters that best answer the statement below the diagram. , Figure 12.2 , Synthesis of DNA takes place ____________________ , Miller & Levine - 12.1-12.2(DNA) - Google Slides DNA's nucleotides are made up of three basic components: a 5-carbon sugar called deoxyribose, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. The nucleotides can be joined together in any order, meaning... PDF 12.1 and 12.2 DNA and DNA Replication - oakparkusd.org 12.1 and 12.2 DNA and DNA Replication, DNA & DNA Replication Nucleotides, ·monomers of DNA ·3 parts, 5-carbon sugar phosphate group nitrogen base, ·4 kinds, pyrimidines - cytosine (C), thymine (T) purines - guanine (G), adenine (A) ·complementary base pairing ·C = G and G = C ·A = T and T = A ·base pairs are connected by hydrogen bonds (H-bonds)
12.2 the structure of dna worksheet answers. 12.2 The Structure of DNA, Chapet 12 Flashcards | Quizlet LOOK AT 12.2 CHART IN NOTES, A 9. nucleotide, 10.nitrogenous base (adenine) hydrogen bonds, deoxyribose sugar, 8. 11. G, C A, G, G C 13. A T, T, C, phosphate group 12. base pair (guanine and cytosine) LOOK AT 12.2 CHART IN NOTES, 14. The drawing below shows half of a DNA molecule. Fill in the appropriate letters for the other half. Chapter 12, DNA - Assessment - Analyzing Data - Page 358: 32 - GradeSaver 12.2 - The Structure of DNA - Analyzing Data, 12.2 - The Structure of DNA - 12.2 Assessment, 12.3 - DNA Replication - 12.3 Assessment, Skills Lab - Pre-Lab - Extracting DNA, Assessment - 12.1 Identifying the Substance of Genes - Understand Key Concepts/Think Critically, 12.2 - The Structure of DNA - Analyzing Data - GradeSaver Chapter 12, DNA - 12.2 - The Structure of DNA - Analyzing Data - Page 345: 3, Answer, Adenine and thymine are complementary, Guanine and cytosine are complementary, Work Step by Step, Since both base pairs appear in the same amount, the conclusion can be drawn that they are complementary. Update this answer! Ch. 12 Chapter Summary - Biology 2e | OpenStax 12.2 Characteristics and Traits, When true-breeding or homozygous individuals that differ for a certain trait are crossed, all of the offspring will be heterozygotes for that trait. If the traits are inherited as dominant and recessive, the F 1 offspring will all exhibit the same phenotype as the parent homozygous for the dominant trait.
7th Science - Ch. 6- Sec. 1 - What does DNA Look Like? Scientist who stated that DNA had equal amounts of adenine and thymine and equal amounts of cytosine and guanine. Her X-ray diffraction images suggested that DNA has a spiral shape. United States geneticist who (with Crick in 1953) helped discover the helical structure of DNA. They used both of Chargaff's & Franklin's discoveries to help prove ... 12.2 structure of dna - Google Slides DNA is a nucleic acid made up of nucleotides joined into long strands or chains by covalent bonds. Nucleic Acids and Nucleotides, Nucleic acids are long, slightly acidic molecules originally... Chapter 12: DNA Damage and Repair - Chemistry - Western Oregon University The integrity of the DNA structure for cell viability is underscored by the vast amounts of cellular machinery dedicated to ensure its accurate replication, repair, and storage. Even still, mutations within the DNA are a fairly common event. ... [reveal-answer q="745512″]Show Answer[/reveal-answer] [hidden-answer a="745512″]Answer b. A ... Biology 2010 Student Edition Chapter 12, DNA - GradeSaver Chapter 12, DNA - Assessment - 12.2 The Structure of DNA - Understand Key Concepts/Think Critically - Page 356: 11, Answer, c. Work Step by Step, Hydrogen bonds form only between adenine and thymine and between cytosine and guanine at the center of the molecule of DNA. This process is called base pairing.
9.1 The Structure of DNA - Concepts of Biology - 1st Canadian Edition Now let's consider the structure of the two types of nucleic acids, deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). The building blocks of DNA are nucleotides, which are made up of three parts: a deoxyribose (5-carbon sugar), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base ( Figure 9.3 ). There are four types of nitrogenous bases in DNA. PDF DNA Review Packet Key to Study - Allegany-Limestone High School Name Class Date Chapter 12.2: The Structure of DNA Lesson Obiectives Identify the chemical components of DNA. Discuss the experiments leading to the identification of DNA as the molecule that carries the genetic code. Describe the steps leading to the development of the double-helix model of DNA. 12.2: Structure of DNA Flashcards | Quizlet Start studying 12.2: Structure of DNA. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Biology 2010 Student Edition Chapter 12, DNA - GradeSaver Assessment - 12.2 The Structure of DNA - Understand Key Concepts/Think Critically, Assessment - 12.3 DNA Replication - Understand Key Concepts/Think Critically, Assessment - Connecting Concepts - Use Science Graphics/Write About Science, Assessment - Analyzing Data, Standardized Test Prep, 13.2 - Ribosomes and Protein Synthesis - 13.2 Assessment,
6 complete the table to describe each scientists - Course Hero Scientist Contribution Erwin Chargaff He revealed that adenine and thymine are usually always equal in DNA Rosalind Franklin She showed the double helix structure of DNA James Watson and Francis Crick Showed how DNA worked. 7. Complete the table by estimating the percentages of each based on Chargaff's rules.
BCR-ABL: Protein Structure and Function - HHMI BioInteractive Description, This tutorial describes the structure and function of the cancer-causing protein BCR-ABL. It also shows how drugs targeting this protein can help treat chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), a cancer of the white blood cells. In CML, white blood cells divide uncontrollably due to an overactive tyrosine kinase protein called BCR-ABL.
PDF Information and Heredity, Cellular Basis of Life Q: What is the ... SAMPLE ANSWER: DNA carries genetic information in its structure, but for a long time, no one knew how. SAMPLE ANSWER: In the 1950s, evidence disclosed the structure of DNA, leading to the double-helix model of Watson and Crick. The model explains how DNA strands are held together. SAMPLE ANSWER: DNA copies itself during mitosis and meiosis.
PDF Lesson 12 - Steelton-Highspire High School Lesson 12.2, Objective Materials Pacing, Identify the chemical components of DNA. Discuss the experiments leading to the identification of DNA as the molecule that carries the genetic code. Describe the steps leading to the development of the double-helix model of DNA. Standards 1 Blocks 0.5, National Standards,
DNA Molecule Label Diagram | Quizlet Phosphate. Molecule found on the side of a DNA molecule. Double Helix. two strands of nucleotides wound about each other; structure of DNA. Thymine. the nucleotide that hydrogen bonds with the nucleotide adenine in DNA. Adenine. the nucleotide that hydrogen bonds with the nucleotide thymine in DNA or with uracil in RNA.
9.1 The Structure of DNA - Concepts of Biology | OpenStax Now let's consider the structure of the two types of nucleic acids, deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). The building blocks of DNA are nucleotides, which are made up of three parts: a deoxyribose (5-carbon sugar), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base ( Figure 9.3 ). There are four types of nitrogenous bases in DNA.
Chapter 12: DNA - Weebly Amoeba Sisters: DNA Replication. DNA INTRO POWERpoint. DNA Replication Powerpoint. 12.1 worksheet. 12.2 worksheet. 12.3 worksheet. DNA extraction lab. DNA Experiments Homework (due 11/9) DNA Replication foldable. Powered by Create your own unique website with customizable templates.
B.12.2 The Structure of DNA | Genetics Quiz - Quizizz Q. Franklin used x-ray crystallography to determine the shape of the DNA molecule is, answer choices, a cloverleaf, a braided rope, a pleated sheet, a twisted ladder, Question 13, 30 seconds, Q. Which of the following best describes a DNA molecule? answer choices, double helix, contains ribose, made of amino acids, contains Uracil, Question 14,
Activity for The Double Helix - HHMI BioInteractive Description. This activity explores the concepts and research presented in the short film The Double Helix, which tells the story of the discovery of the molecular structure of DNA. James Watson and Francis Crick collected and interpreted key evidence to determine that DNA molecules take the shape of a twisted ladder, a double helix.
12.2 Determining Evolutionary Relationships - OpenStax Learning Objectives. Scientists collect information that allows them to make evolutionary connections between organisms. Similar to detective work, scientists must use evidence to uncover the facts. In the case of phylogeny, evolutionary investigations focus on two types of evidence: morphologic (form and function) and genetic.
PDF 12.1 and 12.2 DNA and DNA Replication - oakparkusd.org 12.1 and 12.2 DNA and DNA Replication, DNA & DNA Replication Nucleotides, ·monomers of DNA ·3 parts, 5-carbon sugar phosphate group nitrogen base, ·4 kinds, pyrimidines - cytosine (C), thymine (T) purines - guanine (G), adenine (A) ·complementary base pairing ·C = G and G = C ·A = T and T = A ·base pairs are connected by hydrogen bonds (H-bonds)
Miller & Levine - 12.1-12.2(DNA) - Google Slides DNA's nucleotides are made up of three basic components: a 5-carbon sugar called deoxyribose, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. The nucleotides can be joined together in any order, meaning...
PDF Cell Division Worksheet - lancaster.k12.oh.us 18. Which symbol represents a cell dividing by mitosis? (Circle all that apply) 2n 2n 2n n n n n + n 2n , Use figure 12.2 below to answer the following questions. Write the letter, or letters that best answer the statement below the diagram. , Figure 12.2 , Synthesis of DNA takes place ____________________ ,

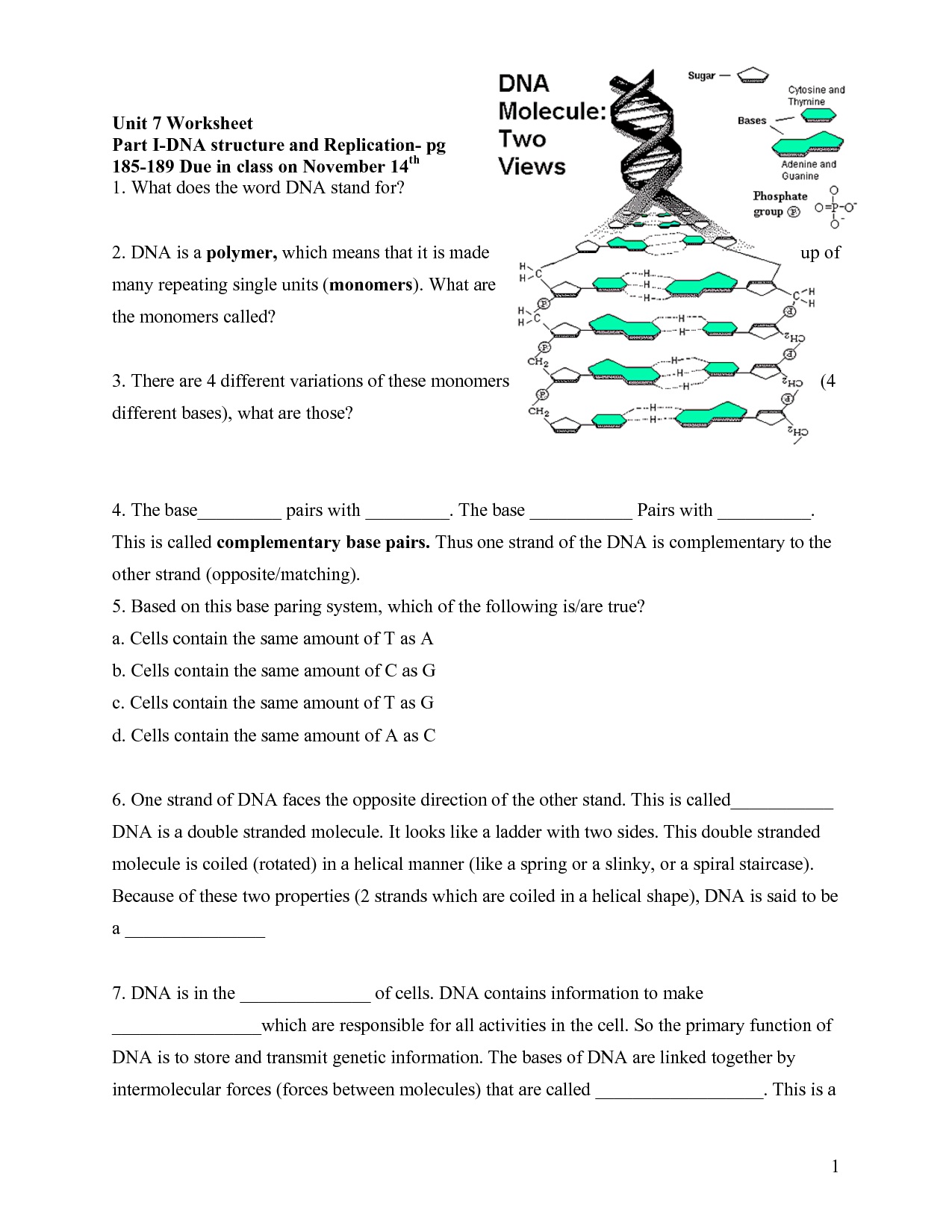













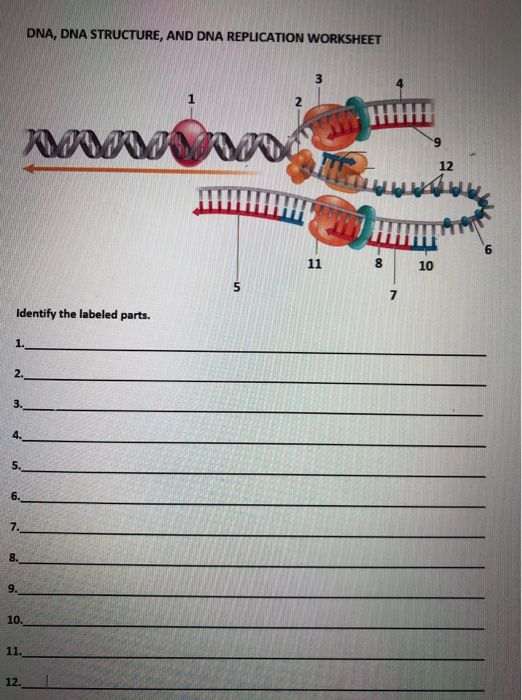



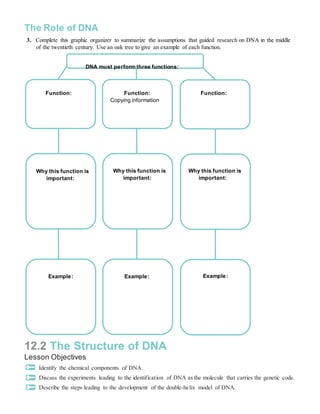









0 Response to "42 12.2 the structure of dna worksheet answers"
Post a Comment